What you need to know about Firewall! The Internet has made much information available to the average computer user at home, in business, and education. For many people, access to this information is no longer just an advantage; it is important.
By connecting a private network to the Internet it can reveal sensitive or confidential information to malicious attacks from anywhere in the world. Attackers may gain access to your sites’ private information or interfere with your use of your systems.
Users who connect their computers to Internetwork should be aware of low-level risks, their consequences, and how to protect their personal information and sensitive systems. Therefore, network security is a key factor here and logs provide this protection.
Internet firewalls keep the flames of an Internet hell out of your network or, keep members of your LAN clean by denying them access to all the worst Internet temptations.
WHAT IS A FIREWALL?

A firewall is simply a program or hardware device that filters information that comes with an Internet connection to your network or computer program.
What Is Application Firewall?
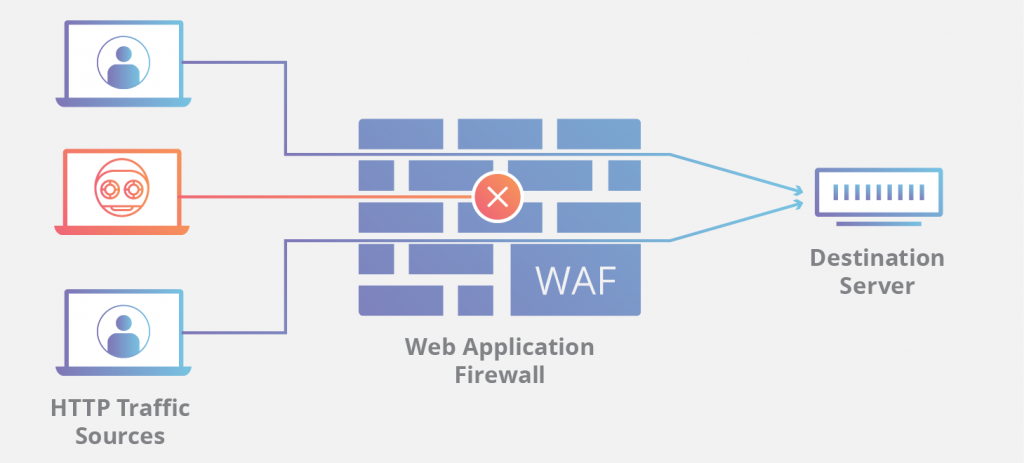

An application firewall is a special firewall specifically written for the type of traffic you are testing. The most advanced application firewall is a web application firewall. The web app’s firewall doesn’t care much about the source and local addresses and focuses on real-time data to see if requests sent to a web server, and responses from a web server, meet its rules. For example, a web application firewall may have a rule that the requested URL may not be more than 256 characters long. When a package with a long URL is found in the application field it can be downloaded without giving it to the webserver.
What Is The Difference Between A Host-Based Firewall And A Network-Based Firewall?
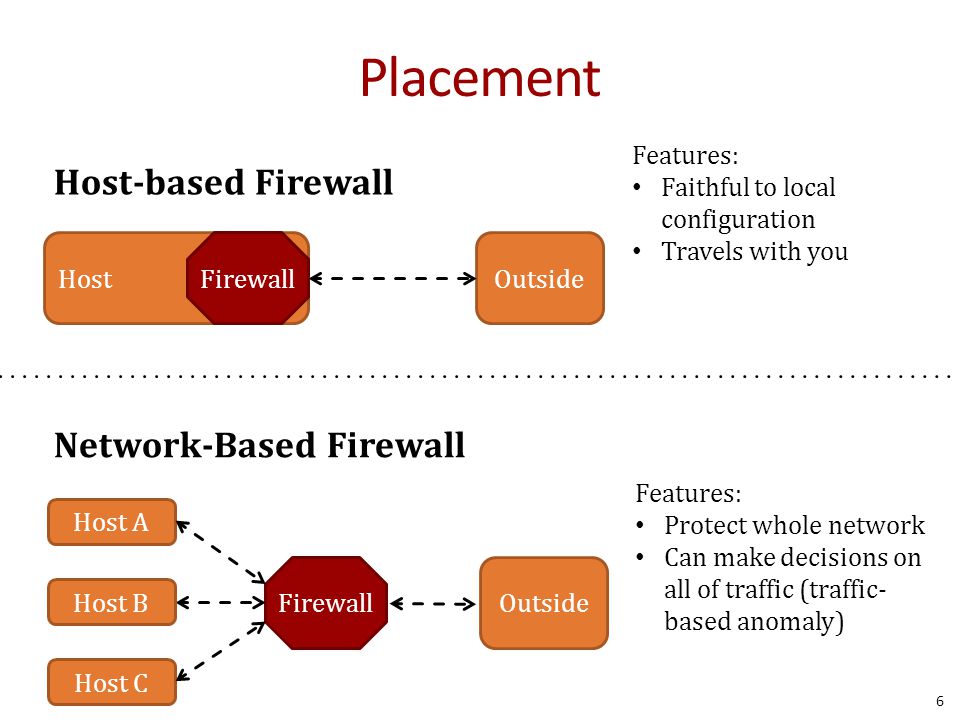

A host-based firewall is installed on each computer to protect it from activities occurring on its network. The policy may affect computer-generated traffic to the Internet, local network, or itself.
A network-based firewall is used somewhere in the network and protects all computers on the “internal” side of the firewall on all computers on the “external” side of the firewall.
A network-based firewall can be installed on the perimeter, or on the edges of the network to protect the company from Internet executives, or internally to protect one part of the community from another, such as separating business and residential systems, or research programs from marketing programs. A network-based firewall cannot protect one computer from another in the same network, or another computer itself.
SOFTWARE FIREWALL VS HARDWARE FIREWALL
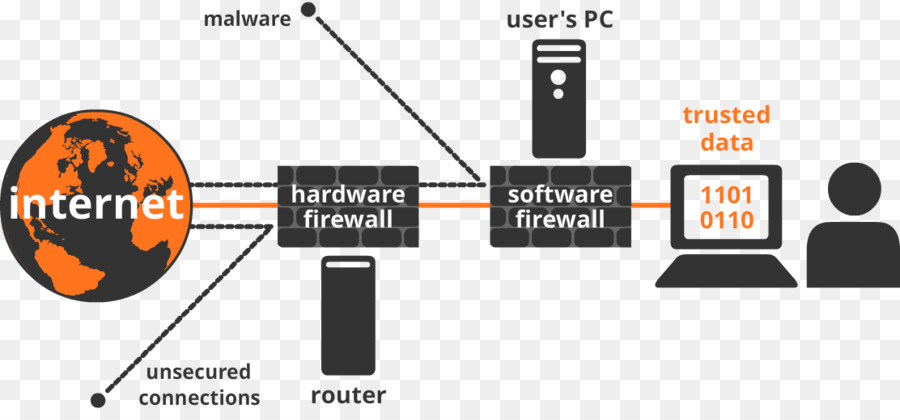

- Software Firewall
Software firewalls are installed on individual servers. They stop each connection request and decide whether the application is valid or not. The software firewall processes all applications through server resources. Apart from the performance limit, a software firewall has many advantages.
Key advantages of a software firewall.
- While comparing with the hardware firewalls, software firewalls are easier to configure and set up.
- .Through the software firewall, we can restrict some specific applications from the Internet. This makes the software firewall more flexible.
- The software firewall gives users complete control over their Internet traffic through a nice user-friendly interface that requires little or no knowledge.
- Hardware Firewalls
Hardware firewalls are connected to a router that sits between a computer and the Internet. They usually use packet filtering, which means they scan the package header to find out their background, origin, address, and destination and look at the user’s existing rules to decide to approve/deny.
Key advantages of hardware firewall.
- Speed: Hardware firewalls are tailored for faster response times, so they can handle more traffic loads.
- Security: A firewall with its operating system is less prone to attacks. This in turn reduces the security risk and in addition, hardware firewalls have enhanced security controls.
- No Interference: Since the hardware firewall is an isolated network component, it can be managed better, and does not load or slow down other applications. The firewall can be moved, shut down, or reconfigured with minimal interference to the network.
History of Firewalls


Firewall technology first appeared in the late 1980s. The Internet was still a relatively new technology in terms of global usage and connectivity. The first theory was developed in response to a major cybersecurity breach, which occurred in the late 1980s. In 1988 an employee of the NASA Ames Research Center in California sent an e-mail invitation to colleagues: “We are currently under attack by the Internet VIRUS! It has attacked Berkeley, UC San Diego, Lawrence Livermore, Stanford, and NASA. Ames.” it was delivered by e-mail and is now a common problem even for an innocent domestic user. Morris Worm was the first major cybersecurity attack, an online community that was unexpected, and unprepared. The online community took the lead in combating any future attacks and began collaborating on new ideas, programs, and software to make the internet safer again. The first paper published in firewall technology was in 1988 when Jeff Mogul of Digital Equipment Corp. developed a filtering system known as package filter filters. This basic program was the first generation of what would become a very emerging online security feature. From 1980-1990 two colleagues from AT&T Bell Laboratories, Dave Presetto, and Howard Trickey, developed the second generation of firewalls known as firewalls at the regional level.
The books by Gene Spafford of Purdue University, Bill Cheswick at AT&T laboratories, and Marcus Ranum described a third-generation firewall application called a layered firewall, also known as proxy-based firewalls. Marcus Ranum’s work in technology led to the creation of the first commercial product. The product is produced by Digital Equipment Corporation’s (DEC) branded as SEAL product. The first major sale of the DEC was on June 13, 1991, to a chemical company based on the East Coast of the USA. At AT&T Bill Cheswick and Steve Bellovin were continuing their research on package filtering and developing their company’s performance model based on their first-generation architecture. In 1992, Bob Braden and Annette DeSchon at the University of Southern California were developing their fourth-generation package fire protection program. The product known as “Visa” was the first system to have a color-coded visual interface, which can be used and easily accessible on a computer program such as Windows Microsoft, or Apple’s Mac / OS. In 1994 an Israeli company called Check Point Software Technologies developed this easily accessible software known as FireWall-1. The second generation of proxy firewalls was based on Kernel Proxy technology. The project is ongoing but its basic features and codes are currently widely used in commercial and home computer programs. Cisco, one of the world’s largest Internet security companies, released the product to the public in 1997.
Design Goals For A Firewall


- The first design goal for a firewall is that collectively the sum of all the network traffic from internal to external must go through the firewall physically cutting off all access to the local network except via the firewall.
- The second design goal would be only authorized traffic which is delineated by the local security policy will be allowed to proceed.
- Finally, the last design goal is that the firewall itself is resistant to penetration inclusive is a solid trustworthy system with a protected operating system.
Types of Firewalls


Three common types of Firewalls:
- Packet-filtering routers
- Application-level gateways
- Circuit-level gateways (Bastion host)
- Packet-Filtering Router
- Applies a set of rules to each incoming IP packet and then forwards or discards the packet
- Filter packets going in both directions
- The packet filter is typically set up as a list of rules based on matches to fields in the IP or TCP header
- Two default policies (discard or forward)
| Advantages of Packet-Filtering Router | Disadvantages of Packet-Filtering Router |
| · Simplicity · Transparency to users · High speed | · Difficulty of setting up packet filter rules · Lack of Authentication |
- Application-level Gateway
- Also called a proxy server
- Acts as a relay of application-level traffic
| Advantages of Application-level Gateway | Disadvantages of Application-level Gateway |
| Higher security than packet filters Only need to scrutinize a few allowable applications Easy to log and audit all incoming traffic | Additional processing overhead on each connection (gateway as splice point) |
- Circuit-Level Gateway
- Sets up two TCP connections
- The gateway typically relays TCP segments from one connection to the other without examining the contents
- Stand-alone system
- The specialized function performed by an Application-level Gateway
- The security function consists of determining which connections will be allowed
- Typically use is a situation in which the system administrator trusts the internal users
- An example is the SOCKS package
Bastion Host
- A system identified by the firewall administrator as a critical strong point in the network´s security
- The bastion host serves as a platform for an application-level or circuit-level gateway
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT FIREWALL
BASIC CONCEPTS OF A FIREWALL
To understand what a firewall is, one can only imagine it in terms of living things as a human organ known as the skin. Skin does not kill hostile foreign bodies, it simply interferes with them. For a person, for example, the loss of more than 50% skin will lead to death, simply because the immune system is unable to repel invaders in a large and exposed area. The same can be said of firewalls that do not have IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems) that can detect hostile attackers but simply reduce their access to your sensitive internal servers.
Well-designed and well-distributed, the firewall acts as a shield around your network like human skin. A firewall operates traffic by its policy. The policy contains a set of rules. A rule is an action performed in traffic that corresponds to a specific procedure. One rule has four basic elements:
SOURCE
- This is where the IP traffic is coming from and is comprised of the following
- Single IP address or multiple IP addresses
- One or more networks in the form of a network ID and subnet mask
- A combination of IP addresses and Network addresses
DESTINATION
- This is where the IP traffic is going to and is comprised of the following
- Single IP address or multiple IP addresses
- One or more networks in the form of a network ID and subnet mask
- A combination of IP addresses and Network addresses
SERVICE
- This is the type of protocol that the traffic is using and is comprised of the following
- One or more destination TCP ports
- One or more destination UDP ports
- A group or combination of destination TCP and UDP ports
- Although the source port can be limited to a certain range, it is generally left wide open. It is the destination port that is primarily specified.
ACTION
- The administrator chooses from the following options if all the above three criteria match
- Reject the traffic
- Drop the traffic
- Permit the traffic
- Encrypt the traffic on IPSEC VPN capable firewalls
THE ROLE OF FIREWALLS


A firewall is a term used for “host”’ between a network of equipment and users operating under the same security policy and who is more trustworthy, as well as the outside world. In recent years, fireworks have become quite popular on the Internet. For the most part, this is because most existing apps are insecure, and are designed under the assumption that the equipment and users will trust each other.
There are two basic reasons for using a firewall right now: saving money on focusing your security on a small number of items, and simplifying system configuration by restricting access to only trusted devices. Firefighters are often viewed as annoying because they are often viewed as an obstacle to accessing resources. This is not a significant mistake of firewood, but rather the result of failure to comply with firewall upgrade requirements.
There is a large enough group of willing and capable people all over the world who are happy to get into the programs. Aside from the feeling of insecurity that has plagued society, the amount of real damage caused is very small. It emphasizes the fact that in reality any system can be disrupted if the enemy is adequately determined. It is a proven and authentic way to improve security within DOD projects so that a “ black hat ” organization tries to break into the systems rather than be found by your real enemies. By bringing system vulnerabilities forward, Internet hackers have provided this service, as well as the impetus to upgrade existing programs. It is probably a simple matter of saying thank you, but I believe it is better to raise these issues at a time when our society will be almost 100% dependent on information systems.
Advantages Of A Firewall
- Extended logging, in which a firewall can concentrate extended logging of network traffic on one system;
- Centralized and simplified network services management, in which services such as FTP, electronic mail, gopher, and other similar services are located on the firewall system(s) as opposed to being maintained on many systems.
- The concentration of security all modified software and logging is located on the firewall system as opposed to being distributed on many hosts;
- Protocol filtering, where the firewall filters protocols and services that are either not necessary or that cannot be adequately secured from exploitation;
- Information hiding, in w hic h a firewall can “hide” name s of internal systems or electronic mail addresses, thereby revealing less information to outside hosts;
- Application gateways, where the firewall requires inside or outside users to connect first to the firewall before connecting further, thereby filtering the protocol;
Disadvantages Of A Firewall
- The most obvious being that certain types of network access may be hampered or even blocked for some hosts, including telnet, FTP, X Windows, NFS, NIS, etc. However, these disadvantages are not unique to firewalls; network access could be restricted at the host level as well, depending on a site’s security policy.
- A second disadvantage with a firewall system is that it concentrates security in one spot as opposed to distributing it among systems, thus a compromise of the firewall could be disastrous to other less-protected systems on the subnet. This weakness can be countered; however, with the argument that lapses and weakness in security are more likely to be found as the number of systems in a subnet increase, thereby multiplying how subnets can be exploited.
- Another disadvantage is that relatively few vendors have offered firewall systems until very recently. Most firewalls have been somewhat “hand-built” by site administrators, however, the time and effort that could go into constructing a firewall may outweigh the cost of a vendor solution. There is also no firm definition of what constitutes a firewall; the term “firewall” can mean many things to many people.
CONCLUSION


The network design that suits your environment depends on the type of application and the risks you are trying to minimize by setting up a secure environment around your servers. As we discussed, relying on a single firewall or merging system tiers on a single subnet often lowers the amount of control you have over how app components are accessed.
One of the best things about a firewall with security is that it prevents anyone outside from accessing the computer on your private network. While this is a big deal for businesses, many home networks will probably not be threatened in this way. However, setting the firewall in place provides peace of mind.
At Palmacedar Limited we deal with network solutions. Get in touch with us today