Cloud Infrastructures promote environmental pro-activity by powering virtual services rather than physical goods and hardware, reducing paper waste, improving energy efficiency, and reducing commuter-related pollution (given that workers can access it from anywhere with an internet connection).

Business Advantages of Cloud Computing

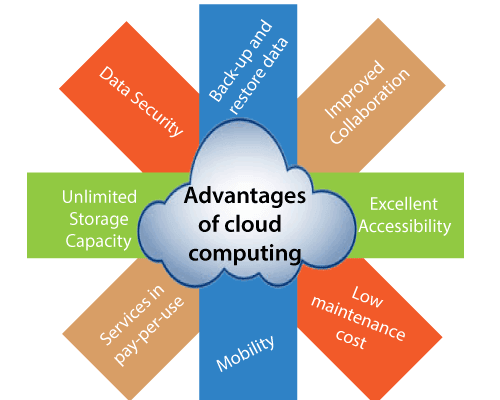
Mobility: Cloud computing enables mobile access to corporate data via smartphones and tablets, which, given the billions of smartphones in use today, is an excellent way to ensure that no one is ever left behind.
Security: When it comes to implementing a cloud-computing solution, several businesses are concerned about stability. Well, 94 percent of companies said transitioning to the cloud improved their security, and 91 percent said it made it easier to meet government enforcement requirements.
Easy data backup: Data loss that is catastrophic can occur at any time. Natural disasters, power surges, or hardware failure may all result in data loss. Although most businesses have contingency plans in place, it is beneficial to have additional contingencies in place.
Quality Control: Few items are as damaging to a company’s success as low quality and inaccurate reporting. Both records are stored in one location and in the same format in a cloud-based framework.
Cost Savings: You’re not alone if you’re concerned about the financial implications of switching to cloud computing. The initial cost of deploying a cloud-based server is a challenge for 20% of businesses.
Automatic Software Updates: There is nothing more inconvenient than having to wait for device updates to be installed while you have a lot on your plate. Cloud-based systems are constantly refreshed and modified.
Sustainability: Given the current state of the atmosphere, it is no longer sufficient for businesses to put a recycling bin in the breakroom and say that they are helping the environment. True sustainability necessitates strategies that fix waste at all levels of a company.
Data that is extremely accessible: Businesses use cloud storage to access information from any computer that can connect to the internet.
Insight: When we move further into the digital era, it becomes increasingly clear that “data is wealth.” There are nuggets of useful, actionable knowledge hidden in the millions of bits of data that accompany your consumer transactions and business operation, just waiting to be discovered and acted upon.

Cloud computing is an umbrella term for different types of cloud services, including:
Cloud backup: Although cloud storage and cloud backup can appear to be the same thing, cloud backup is intended to be a failsafe solution in the event of a server crash, cyberattack, or other data loss.
Cloud hosting: Email services, application hosting, web-based phone systems, and data storage are just a few of the forms of information sharing that these technologies provide.
Cloud storage: These services save and back up your files so you can access them whenever you want. Files may also be exchanged and synchronized between different devices.
Infrastructure as a service: Physical hardware, such as in-house web hosting servers, is replaced by infrastructure as a service. Infrastructure as a service allows companies to take advantage of a variety of configurations to handle various workload needs by delivering items like virtual servers or virtual machines.
Software as a service (SaaS): SaaS applications make use of the internet to provide a service. Office 365, Google Apps, QuickBooks Online, and Salesforce are examples of Software as a Service applications. Platform as a service solution are similar to software as a service solution.